angiography
What is eye angiography?
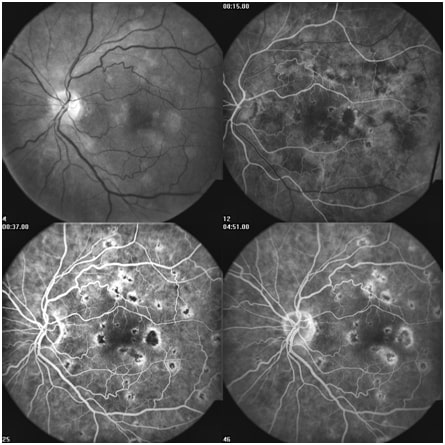
The angiography device is, in fact, an advanced camera capable of capturing images of the retina (the back of the eye). Using fluorescein dye, color images (fluorescein angiography) of the retina can be obtained, allowing the surgeon to identify and treat blood vessel abnormalities in the retina. This device is most commonly used in patients with diabetes, high blood pressure, various retinal conditions (such as CRVO, BRVO, CRAO, BRAO), and retinal tumors.
In eye angiography, the blood vessels of the retina and the blood flow within these vessels are imaged. To enhance the clarity of these vessels during imaging, eye drops are instilled that temporarily dilate the pupil. This causes temporary blurriness, which typically resolves after a few hours.
The dilation of the pupil takes approximately 20 minutes. After these stages, the patient sits in front of the camera, and a nurse begins taking pictures of the retina. To enhance the visibility of retinal blood vessels, a red-colored dye is injected into the patient’s hand. This test typically causes no pain or adverse effects. It’s important to note that due to the injection of this substance, the color of the urine and skin may temporarily turn yellow, which resolves after a few hours and increased fluid intake.
After the images appear and are reviewed by the treating physician, the results will be communicated to the patient for further examinations or potential laser treatments.
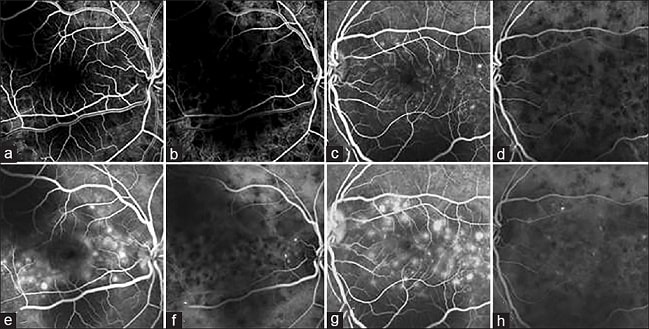
To perform this test, an injection of Fluorescein or Indocyanine green (ICG) is administered into a vein in the arm, and a fundus camera is used to capture images of the back part of the eye. This test is used to examine the blood flow in the retina and the choroidal vessels. Typically, Fluorescein angiography is used to assess conditions like diabetic retinopathy, vascular occlusive diseases such as retinal artery or vein occlusion, and the evaluation of wet macular degeneration. ICG is more commonly used to examine blood flow in the macula.
The device is equipped with two laser sources with wavelengths ranging from 400 to 500 nanometers and an infrared laser source. The two primary lasers are sensitive to the mentioned dyes, and these dyes reflect the light effectively, making the blood vessels clearly visible.
